More benefit in the treatment of diabetes from modern insulin
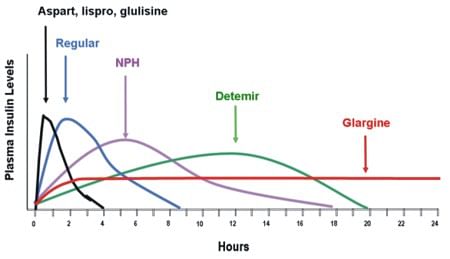
Plasma level of different insulins after administration into subcutaneous tissue over time. The figure shows the safety of insulin aspart in comparison to other insulins
Modern insulins (also called insulin analogues) are genetically engineered, modified insulins that have changed treatment by insulin and improved blood glucose control in diabetes patients.
The development of modern insulin represents a significant advance in the management of diabetes. The treatment regimens can now be tailored to meet an individual's need. They reduce the incidence of hypoglycaema (low concentration of glucose in the blood), are easily administered by almost painless injections with a convenient device.
Modern insulin provide advantages of treatment for both insulin-naïve patients and those patients currently being managed unsuccessfully with older, traditional insulins as well as significant health economic benefits.
Blood sugar after food intake remains high in most people using conventional human insulin. Because conventional human insulin is absorbed into the blood slowly after injection in subcutaneous tissue.
To bypass this slow absorption rate and avoid raised blood glucose after food intake, regular human insulin is recommended to be injected 30 minutes before a meal. Many diabetic patients do not consider the importance of timing in administering their insulin injections. Instead, they elect to inject insulin at more convenient but inappropriate times.
Inappropriate timing of insulin administration results in a mismatching of carbohydrate absorption after food and post-injection insulin peak. Regular human insulin is still present in the blood when insulin is not needed. This often does not fit with patient's lifestyle and the mismatch also predisposes patients to the development of acute complications of diabetes such as hypoglycaemia (blood glucose level below the lower limit of the normal range). It also places patients at risk for long-term complications in kidney, eye, cardiovascular and nervous system.
On the other hand, modern insulin is absorbed at once into the body and start works very rapidly. So after injection, patients need not wait for 30 minutes to take food.
NovoMix 30 and NovoRapid are two modern insulins that have launched by Novo Nordisk very recently in Bangladesh from which diabetic patients will get this benefit.
NovoRapid is a rapid acting modern insulin and its generic name is insulin aspart. It is absorbed rapidly after subcutaneous injection as it breaks down very rapidly in absorbable form.
Clinical studies have shown that NovoRapid has twice as rapid onset of action and reaches a higher peak than soluble human insulin in a shorter span of time. Therefore it provides better blood glucose control after food intake with low risk of hypoglycemia.
The action of insulin aspart lasts for only 3-5 hours unlike soluble human insulin whose action lasts up to 8 hours after the injection into the subcutaneous tissue.
NovoMix 30 is the combination of insulin aspart and longer acting insulin aspart in 30:70 ratio. To fulfill the need for better premixed insulins and considering the fact that premixed insulins are the most widely used insulins, especially in management of type 2 diabetes, premix insulin aspart was developed. In the premix formulations rapid acting insulin aspart care the raised blood glucose after food whereas the longer acting insulin aspart component provides basal coverage. Thus this premix analogue provides not only effective control of postprandial hyperglycemia (raised blood glucose above the normal limit) but also fasting hyperglycemia. The efficacy and safety of this premixed modern insulin NovoMix 30 has been widely studied in various populations.
Modern insulins have made possible the near-physiological replacement of insulin need after food intake as well as basal need.
The proper use of modern insulins allows people with diabetes greater flexibility in the timing of meals, snacks, and exercise, which in turn enhances their ability to lead normal lives.
Their availability will help treatment strategies to be tailored to the needs of individual patients thereby helping them to achieve the best possible blood glucose control.
Modern insulins will also provide physicians with the appropriate tools to overcome the obstacles to improve blood glucose control and subsequently improve diabetes outcomes.
The writer is a Professor of Endocrinology & Diabetology of BIRDEM.

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 



Comments