New regulations in the offing to tackle e-money fraud
The banking regulator is expected to soon introduce new regulations to ensure transparency and discipline in the issuance of e-money and tackle fraud using virtual money, according to officials familiar with the matter.
Titled 'Regulation for E-Money Issuers in Bangladesh-2025', the new rules are set to come in the backdrop of reports of embezzlement by mobile financial services (MFS) provider Nagad through the fraudulent issuance of Tk 645 crore in e-money without maintaining the required currency reserve.
Currently, banks, MFS providers, and payment service providers (PSPs) are allowed to issue e-money, provided it is backed by adequate cash funds.
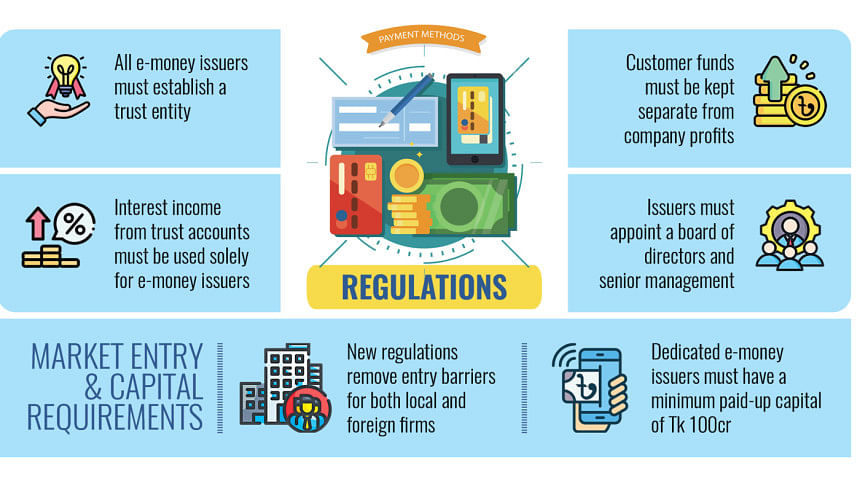
Under the new regulations, an e-money issuer must establish a trust entity under the Trusts Act, 1882, according to a draft seen by The Daily Star, prepared by a committee of the Payment Systems Department. The trust entity will be the custodian of trust and settlement accounts, which hold the balances against which e-money is created.
At present, e-money issuers like MFSs and PSPs maintain trust and settlement accounts with different banks but do not have a trust entity.
Under the proposed regulations, such accounts will hold only the money paid for e-money by e-money account holders and will not be blended with the capital, working capital, or operating funds of the issuer, a senior official of Bangladesh Bank explained to The Daily Star.
"The funds held in the trust settlement account may earn interest or be invested in government securities at a certain percentage.
"This would generate interest income, and at least 80 percent of this interest income must be spent on the operations of the e-money system, with the aim of reducing operational costs," the official, speaking on condition of anonymity, said.
This money cannot be used for bonuses, marketing campaigns, or any similar expenses, they added.
Currently, only banks and government enterprises are able to set up e-money issuers, such as bKash, Nagad, and Rocket. But in the new regulations, barriers to entry into the e-money business have been removed from the previous bank-led or government enterprise model.
Any local or international firm, subject to compliance with the criteria in the guideline, can apply to the central bank for an e-money issuer licence, as per the draft regulations.
The BB official said the new regulations would encourage the integration of innovation by fintech firms in the e-money business to pave the way for a cashless Bangladesh.
"This is expected to increase competition, expand e-money services to all possible use cases, and reduce costs through expansion of the ecosystem. It will also help tackle fraud," they added.
Furthermore, under the new regulations, e-money issuers can operate in three modes. First, PSP (Payment Service Provider), which presently provides e-wallet services except for cash-in and cash-out services.
Second, authorised e-money issuers, operated as a business unit of a scheduled bank or financial institution with the ability to provide full-fledged e-wallet and e-money services, including cash-in and cash-out facilities.
Third, dedicated e-money issuers, which are separate corporate entities with the ability to provide full-fledged e-wallet and e-money services, including cash-in and cash-out facilities.
"There will be separate capital requirements for each type of entity, and all e-money issuers must be incorporated in Bangladesh," reads the draft regulations.
The paid-up capital of a dedicated e-money issuer will be Tk100 crore to get a central bank licence, it adds.
The draft further states that the board of directors, senior management, and risk management have been introduced for the first time to promote good governance and trust in the system.
The e-money issuers will make it explicit in their memorandum of association that the e-money balances kept in the trust and settlement accounts will be unencumbered.
The regulations are also set to introduce comprehensive standards regarding technology management, agent management, outsourcing arrangements, etc.
All e-money operations, including prepaid cards, travel cards, etc., in domestic or foreign currency, will come under the supervision of these regulations, it states.
The definition of e-money has been specified as "electronic money", including magnetically stored monetary value as represented by a claim on the issuer, which is issued on receipt of funds, redeemable against cash, and accepted by a natural or legal person other than the e-money issuer.

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 



Comments